Why do elderly people fall and break bones easier than young people?
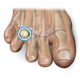
Neuroma Foot Treatment
May 1, 2024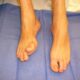
What is Brachymetatarsia?
May 1, 2024Elderly people are more prone to falls and fractures compared to younger individuals due to a combination of factors related to aging and age-related changes in the body. Some of the main reasons include:
- Decreased Bone Density: As people age, their bones naturally become less dense, making them more susceptible to fractures. This decrease in bone density is especially significant in post-menopausal women due to hormonal changes that affect bone health.
- Muscle Weakness: Aging is associated with a gradual loss of muscle mass and strength, a condition known as sarcopenia. Weaker muscles can impair balance and stability, increasing the risk of falling.
- Reduced Flexibility and Range of Motion: Aging can lead to a decrease in joint flexibility and range of motion, which can affect gait and balance and contribute to falls.
- Impaired Balance and Coordination: Age-related changes in the inner ear and other sensory organs can affect balance and coordination, making it more challenging to maintain stability while walking or standing.
- Vision Changes: Elderly individuals may experience visual impairments such as decreased acuity, depth perception, and peripheral vision, which can increase the risk of misjudging obstacles and hazards.
- Medications: Many elderly individuals take multiple medications, some of which can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, or sedation, leading to an increased risk of falls.
- Chronic Health Conditions: Certain chronic healthconditions such as arthritis, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke can affect mobility, balance, and coordination, making falls more likely.
- Environmental Hazards: Elderly individuals may encounter environmental hazards in their living spaces, such as slippery floors, poor lighting, or obstacles, which can increase the risk of falls.
- Impaired Reaction Time: Aging can lead to a decline in cognitive function and slowed reaction times, making it more challenging to respond quickly to potential fall hazards.
- Comorbidities: Older individuals are more likely to have multiple medical conditions, which can affect their overall health and increase the risk of falls.
Due to these factors, falls among the elderly can have more severe consequences, including fractures and other serious injuries. Preventive measures such as regular exercise to maintain muscle strength and balance, vision checks, modifying the home environment to reduce hazards, and medication review can help reduce the risk of falls and fractures in the elderly population. It’s essential for older individuals and their caregivers to be proactive in taking steps to prevent falls and promote overall safety and well-being.



