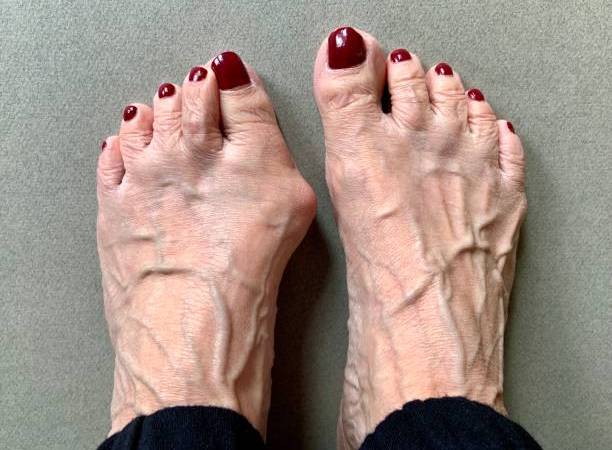
Why do I have Bunion Pain?
What to Expect During Your Recovery After an Ankle Surgery?
May 24, 2024
Painful Crooked Toes
June 4, 2024Bunions are a common foot deformity characterized by a bony bump that forms at the base of the big toe. This condition often develops gradually, causing the big toe to deviate towards the other toes, resulting in pain, inflammation, and difficulty wearing shoes. While genetics play a significant role in predisposing individuals to bunions, other factors such as wearing tight or narrow shoes and certain foot structures can exacerbate the condition.
Managing bunions involves a combination of conservative measures and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Wearing shoes with a wide toe box and low heels can alleviate pressure on the bunion and reduce discomfort. Custom orthotics or padding may also provide additional support and cushioning. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain and inflammation.
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief or the bunion becomes increasingly painful and affects daily activities, surgical correction may be necessary. Bunion surgery aims to realign the bone, restore normal toe function, and relieve pain. However, surgery is typically considered a last resort and should be discussed with a podiatrist or orthopedic surgeon after exploring conservative options.
Regular monitoring and early intervention can help manage bunions effectively, preventing further progression and improving quality of life. By adopting proper foot care practices and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can alleviate pain and maintain foot health.